Main Body
Prokaryotic Translation
Prokaryotic Translation
Dr.V.Malathi
Translation
- Translation is the last step in gene expression,
- During translation the coding sequence of mRNA is translated into the amino-acid sequence of a protein.
- Translation is a highly dynamic process and comprises four major phases: initiation, elongation, termination, and ribosome recycling.
- Ribosomes form transient complexes with auxiliary translation factors during each phase of translation and facilitate protein synthesis.
Translation in Prokaryotes
- In bacteria, translation initiation occurs co transcriptionally. The RNA polymerase (RNAP) and the ribosome physically interact with each other.
- The ribosome binds to the ribosome binding site (RBS) of the mRNA as soon as it emerges from the RNAP.
Initiation
- During translation initiation, the ribosome recruits an mRNA and selects the start codon of the Open Reading Frame (ORF)
- m RNAS of prokaryotes have an extended 5′ untranslated region (5′UTR) and an Shine- Dalgarno sequence (SD) located 8–10 nt upstream of the start codon (usually AUG).
- Interactions between the SD sequence and the complementary anti-SD (aSD) sequence in 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) recruits the small 30 S ribosomal subunit and anchors the 30S ribosomal subunit at the correct location on the mRNA template.
- Initiation is promoted by initiation factors IF1, IF2, and IF3. IF1 enhances the activities of IF2 and IF3.IF2 is a GTPase that recruits the initiator fMet-tRNAfMet. IF3 interferes with subunit association. It also ensures the fidelity of fMet-tRNAfMet selection over the elongator aminoacyl-tRNAs (aa-tRNAs), and helps to discriminate against mRNAs with unfavorable translation initiation regions (TIRs)
- The initiator tRNA then interacts with the start codon AUG (or rarely, GUG). This tRNA carries the amino acid methionine, which is formylated after its attachment to the tRNA and thus the Charged t RNA , fMet-tRNAMetf is formed . This is mediated by the initiation factor IF-2.
- The initiating fMet is usually removed after translation is complete.
- After the formation of the initiation complex, the 30S ribosomal subunit is joined by the 50S subunit to form the 70S translation complex.
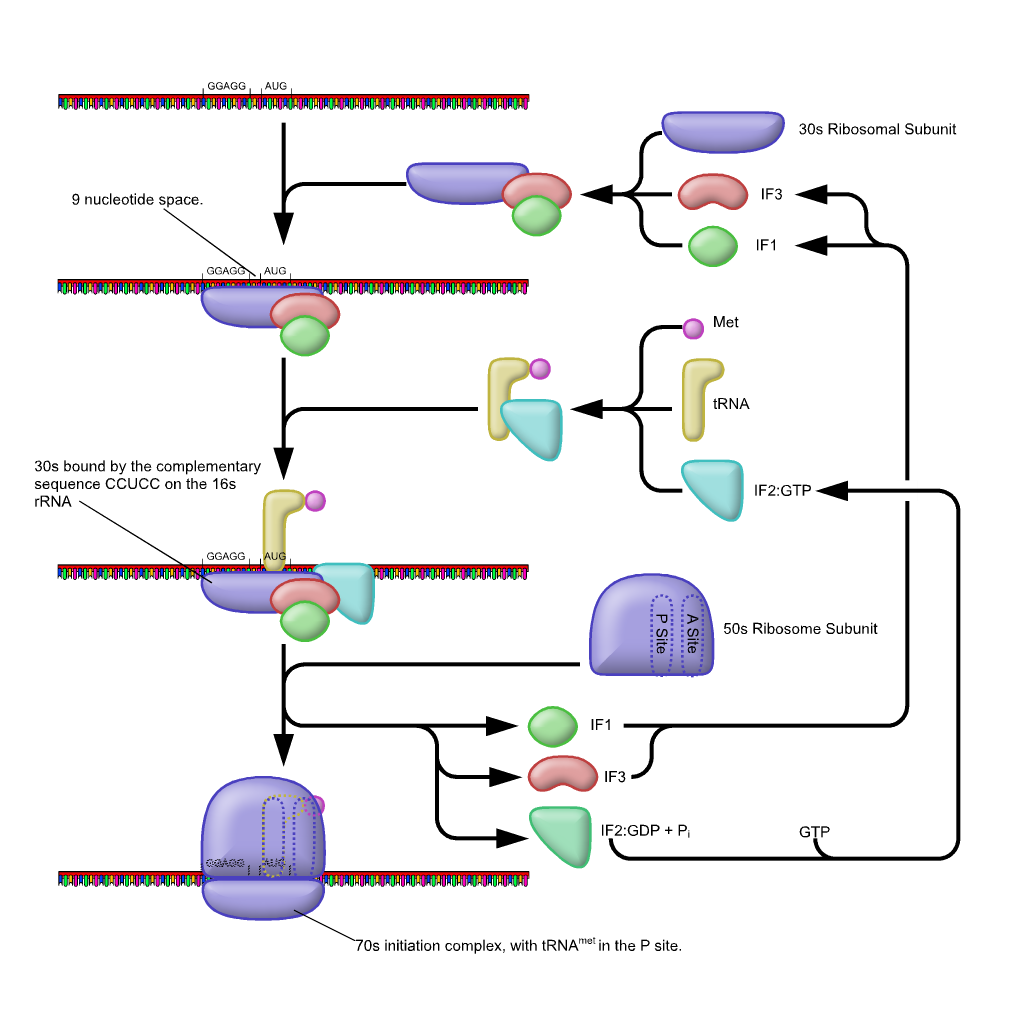
“Prokaryotic Translation Initiation” by Richard Wheeler (Zephyris) via wikimedia is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0
- The ribosome consists of three compartments.
- The A (aminoacyl) site : the incoming charged aminoacyl tRNAs binds to this site.
- The P (peptidyl) site : binds charged tRNAs carrying amino acids that have formed peptide bonds with the growing polypeptide chain but have not yet dissociated from their corresponding tRNA.
- The E (exit) site : The uncharged t RNA ( t RNA after delivering the aminoacid) are released from this site.
definition
The nucleotide sequence located 8-10 nucleotides upstream of the start codon.Interaction between the complementary anti-SD sequence in 16S ribosomal RNA recruits 30S ribosomal subuni at the correct location on the m RNA

