Main Body
Eukaryotic Translation-Initiation
Eukaryotic Translation-Initiation
Dr.V.Malathi
The process of initiation can be grouped in to 4 main headings as
- Ribosome dissociation in to 40 S and 60 S
- Ternary complex called pre initiation complex formation – initiator t RNA +GTP+ eIF2+40S ribosomal subunit
- mRNA binding to preinitiation complex
- 60S ribosomal subunit binding to the complex
The steps in the process of initiation
The steps can be summarized as :
- GTP binds to eIF2- Binary complex
- eIF2 composed of 3 subunits – α, β and γ.
- Binary complex binding to initiator t RNA
- Binding of 40S ribosomal subunit
- Ternary complex – called 43S preinitiation complex. This complex is stabilized by earlier association of eIF3 and eIF1 to the 40S subunit
- Eukaryotes does not require the Shine-Dalgarno sequence rather the eukaryotic initiation complex recognizes the 7-methylguanosine cap at the 5′ end of the mRNA.
- Cap structure of mRNA is bound by eIFs prior to pre initiation complex formation. Cap binding accomplished by e IF -4F
This factor is a complex of 3 proteins namely eIF-4E, A and GeIF-4E – 24 KDa protein, recognizes and binds cap structureeIF-4A – 46 KDa protein, binds and hydrolyses ATP , exhibits RNA helicase activity, resolves RNA secondary structures.eIF- 4G – helps in the binding of mRNA to 43S preinitiation complex
- The cap-binding protein (CBP) and IFs assist the movement of the ribosome to the 5′ cap. Once at the cap, the initiation complex moves along the mRNA in the 5′ to 3′ direction, searching for the AUG start codon.
- Many eukaryotic mRNAs are translated from the first AUG, but this is not always the case.
- According to Kozak’s rules, the nucleotides around the AUG indicate whether it is the correct start codon. state that the following consensus sequence must appear around the AUG of vertebrate genes: 5′-gccRccAUGG-3′. The R (for purine) indicates a site that can be either A or G, but cannot be C or U. Sequences closer to this consensus show higher efficiency of translation.
- e IF-5 binds to preinitiation complex. This is followed by the binding of initiator t RNA – met –tRNA met to the AUG codon of mRNA ( process helped by eIF-1)
- This is followed by the binding of 60S subunit and results in the formation of 80S complex.
- Association of 60S requires e IF-5.Energy for the binding dervied by GTP hydrolysis – bound to eIF-2.
-
eIF-2 cycle
•GDP bound form of eIF-2 binds to e IF-2B
•eIF-2B stimulates exchange of GTP for GDP( therefore called GEF-Guanine nucleotide exchange factor).
•eIF-2B dissociate from eIF-2
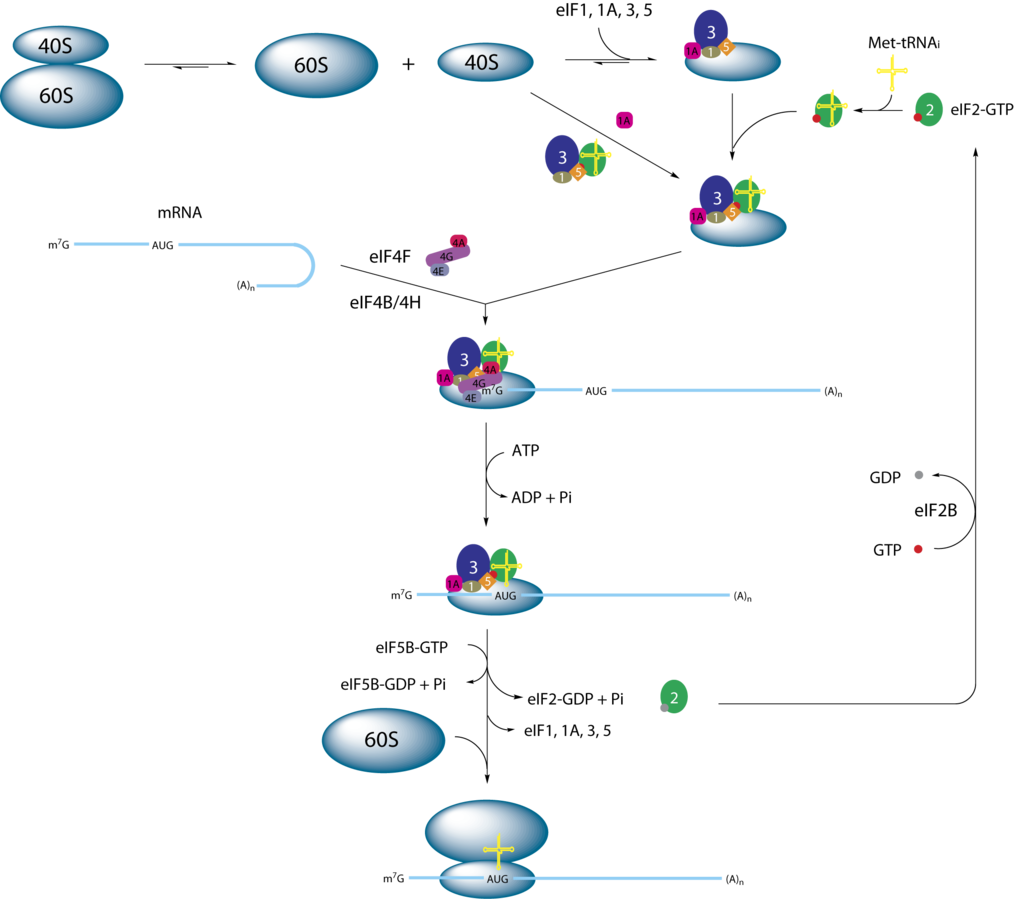
“Eukaryotic Translation Initiation” by Webridge via wikemedia is licensed under CC BY 3.0
State that the consensus sequence 5' -gccRccAUCC-3' must appear around AUG of vertebrate genes. Sequences closer to this consensus show higher efficiency of translation

