Main Body
Chapter 1 : What are Genes?
Genes- Characteristics and Function
Dr.V.Malathi
Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, readers will be able to:
- Discuss what are genes?
- Explain the organization of genes in Prokaryotes
- Discuss the organization of genes in Eukaryotes
- Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene Organization
- Explain what are chromosomes, their types and function
1. Genes-Characteristics and Function
Genes are the basic unit of inheritance containing the information for physical and biological traits. They contain the information necessary for living cells to survive and reproduce . Genes are regions of the DNA .They are passed from parents to offspring. They code for specific proteins or segments of proteins. Humans have approximately 20,000 protein coding genes . These 20,000 protein coding genes are encoded only 1.5% of the entire human genome. Not all genes code only for proteins , some genes encode information for making an RNA molecule that functions other than directly coding for a protein.
Genes in genome of eukaryotes consist of exons and introns. Exons are the protein coding regions of mRNA. These are the regions that contain information for making a protein whereas other regions of the RNA are non-coding and these regions are called introns
The majority of human genes have two or more possible alleles, which are alternative forms of a gene. Differences in alleles account for the considerable genetic variation among people. In fact, most human genetic variation is the result of differences in individual DNA bases within alleles.
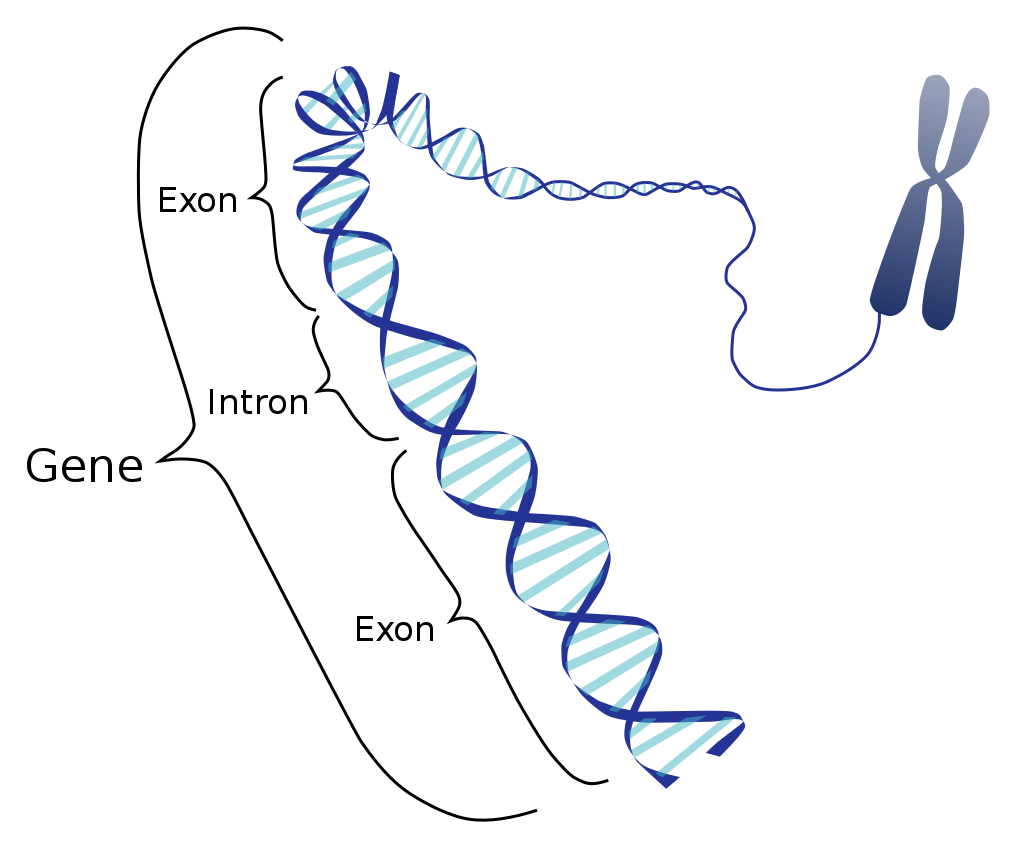 “Gene_Intron_Exon” by Smedlib via Wikimedia commons is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
“Gene_Intron_Exon” by Smedlib via Wikimedia commons is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
These are the protein coding sequences of mRNA
These are the intervening , non coding sequences of m RNA
These are alternative forms of a gene. Differences in alleles account for the considerable genetic variation among people.

