Main Body
Initiation of Transcription by RNA Polymerase
Initiation of Transcription by RNA Polymerase II
Dr.V.Malathi
Transcription Factors
RNA polymerase II requires specific proteins called transcription factors to initiate transcription .
Two general types of transcription factors have been defined namely ;
- General transcription factors : These are involved in transcription from all polymerase II promoters and part of the basic transcription machinery.
- Additional transcription factors : These bind to DNA sequences that control the expression of individual genes and regulate gene expression.
Enhancers
Enhancer regions are binding sequences, for specific transcription factors. Enhancers may be located upstream or downstream of transcription start site. Each enhancer is made up of short DNA sequences called distal control elements .
Proteins called Activators , mediator proteins and transcription factors bind to the enhancers .When a transcription factor binds to its enhancer sequence, the shape of the transcription factor protein changes. This enables the transcription factor to interact with proteins at the promoter site.
As the enhancer region may be distant from the promoter, the DNA must bend to allow the proteins at the two sites to come into contact. DNA bending proteins help to bend the DNA and bring the enhancer and promoter regions together.
Two different genes may have the same promoter but different distal control elements, enabling differential gene expression.
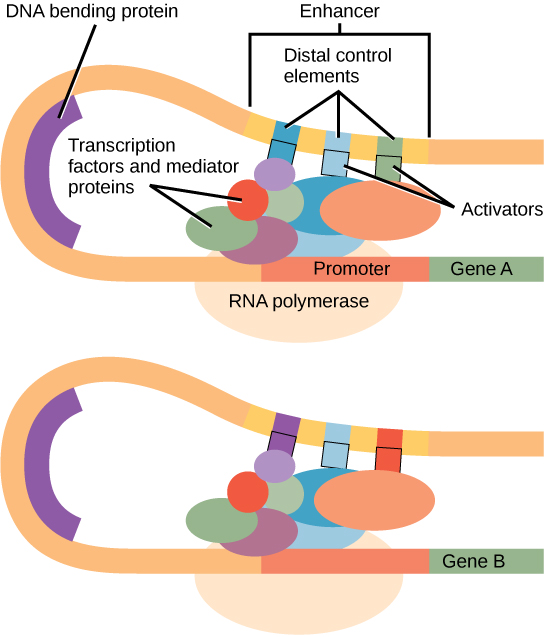
“Enhancers” image from Biology, an OpenStax resource is licensed under CC BY 4.0
The promoters of RNA polymerase II
The TATA box : This resembles the the -10 sequence element of bacterial promoters. This region contain the sequence TATAA and is located 25 to 30 nucleotides upstream of the transcription start site.
Initiator, or Inr, sequence : In addition to the TATA box , the promoters of many gene contain a second important sequence element called initiator, or Inr, sequence. Some RNA polymerase II promoters contain only an Inr element, with no TATA box.
The promoter -proximal elements : The CAAT box, with the consensus sequence 5’-CCAAT-3’ and the GC box, with the consensus sequence 5’-GGGCGG-3’. These promoter-proximal elements regulate gene transcription.
Initiation-Formation of the Transcription complex
- The first step in formation of a transcription complex is the binding of a general transcription factors called TFIID to the TATA box.TFIID is itself composed of multiple subunits, including the TATA binding protein . This binds specifically to the TATAA consensus sequence .and 10-12 other polypeptides, called TBP-associated factors (TAFs).
- TBP then binds a second general transcription factor (TFIIB) forming a TBP-TFIIB complex at the along with TF II F at the promoter
- Then RNA polymerase II binds
- This is followed by the binding of TFIIE and TFIIH.
- TFIIH is a multi subunit factor. It plays two important roles. First, two subunits of TFIIH are helicases, which unwind DNA around the initiation site. These subunits of TFIIH are also required for Nucleotide excision repair .Another subunit of TFIIH is a Protein kinase . This phosphorylates repeated sequences present in the C-terminal domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II.
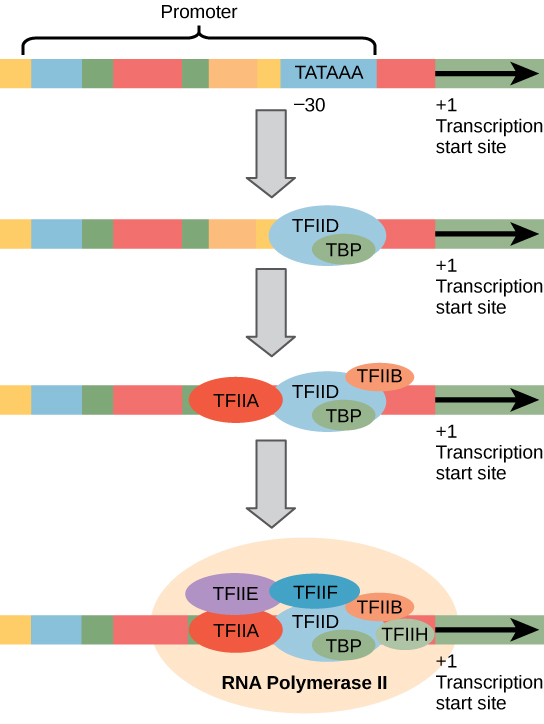
“Eukaryotic Transcription Initiation” image from the book General Biology (Boundless) licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
- Once the complex is assembled, RNA polymerase can bind to its upstream sequence.
- When bound along with the transcription factors, RNA polymerase is phosphorylated. This releases part of the protein from the DNA . The transcription initiation complex gets activated and places RNA polymerase in the correct orientation to begin transcription.
- Then the double-stranded DNA in the transcription start region is unwound . The RNA Polymerase II is then positioned at the +1 initiation nucleotide and starts new RNA strand synthesis.
These are binding sequences for transcription factors and may be located upstream or down stream of transcription start site

