Main Body
Chapter 2- What is Gene expression?
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
Dr.V.Malathi
Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, readers will be able to:
- Discuss flow of information in biological systems
- Explain the process of Transcription and Translation in Prokaryotes
- Discuss about Eukaryotic Transcription and Translation
- Analyze the importance of Transcription and Translation .
Gene Expression
The process of turning on a gene to produce RNA and protein is called gene expression. For a cell to function properly appropriate proteins must be synthesized at the appropriate time. Whether in a simple unicellular organism or a complex multi-cellular organism, each cell controls when and how its genes are expressed.
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology -Information flow in biological systems
The central dogma of molecular biology explains the flow of genetic information within a biological system. It is often stated as “DNA makes RNA, and RNA makes protein” .
- DNA can be copied to DNA through a molecular process called DNA Replication. Instructions for making proteins with the correct sequence of amino acids are encoded in DNA.
- This information in DNA can be copied into RNA through the molecular process called Transcription by which the information in the DNA of every cell is converted into small, portable RNA messages.
- Proteins can be synthesized using the information in mRNA as a template through the molecular process called Translation. During translation, the RNA messages travel from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm where they are ‘read’ to make specific proteins.
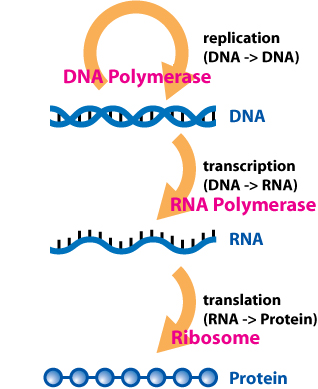
Image of “An overview of the (basic) central dogma of molecular biochemistry” by Dhorspool at en.wikipedia is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0
The process of turning on a gene to produce RNA and protein
The molecular process by which the information in DNA is copied in to RNA. This process is carried out in the nucleus of the cell
The process by which the information in mRNA is decoded forming protein. This is carried out in the cytoplasm of the cell

