1. Cell structure and Function
1.5. Cell Organelles
Plant organelles
Dr V Malathi and Mrs Sushumna Rao
Organelles are structures found within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cell. Each organelle is enclosed within a membrane and performs a specific function.
Organelles in animal cells include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, vacuoles etc .,
Ribosomes are not enclosed within a membrane but are still commonly referred to as organelles in eukaryotic cells.
Organelles/ cell structures specific for plant cell
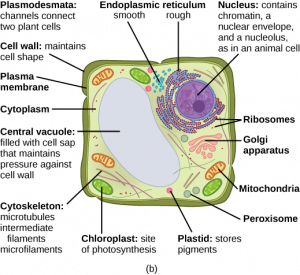
“plant cell” by OpenStax is licensed under CC BY 4.0
The Cell Wall
The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell,
It provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell.
Fungal and protistan cells also have cell walls.
The plant cell wall is mainly composed of an organic constituent called cellulose, a polysaccharide comprised of glucose units.
While the chief component of prokaryotic cell walls is peptidoglycan,

Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are plant cell organelles that carry out photosynthesis
They have their own DNA.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants through a series of reactions use carbon dioxide, water, and light energy to make glucose and oxygen.
Plants are autotrophs as they are able to make their own food, like sugars, while animals are heterotrophs as they must ingest their food.
This is a major difference between plants and animals;
Chloroplasts have outer and inner membranes
Within the space enclosed by a chloroplast’s inner membrane there is a set of interconnected and stacked fluid-filled membrane sacs called thylakoids.
Each stack of thylakoids is called a granum (plural = grana).
The fluid enclosed by the inner membrane that surrounds the grana is called the stroma.
The space inside the thylakoid membranes is called the thylakoid space.
The chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which captures the light energy for carrying out the process of photosynthesis.
The light harvesting reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes.
The synthesis of sugar takes place in the stroma.
Like plant cells, photosynthetic protists also have chloroplasts. Some bacteria perform photosynthesis, but their chlorophyll is not relegated to an organelle.
“Chloroplast structure” by OpenStaxis licensed under CC BY 4.0
The Central Vacuole
The central vacuole is an unique and essential component of plant cell and occupies most of the space of the cell.
The central vacuole plays a key role in regulating the concentration of water in the cell against the changing environmental conditions.
The the liquid inside the central vacuole provides turgor pressure, which is the outward pressure caused by the fluid inside the cell.
The wilting of a plant when we forget to water it for few days is because of shrinking of the central vacuole caused due to the movement of water out of the central vacuole ,as the water concentration in the soil becomes lower than the water concentration in the plant.
This loss of support to the cell walls of plant cells results in the wilted appearance of the plant.
On the contrary when the central vacuole holds more water, the cell gets larger without having to invest a lot of energy in synthesizing new cytoplasm.
The fluid inside the central vacuole has a very bitter taste, which discourages consumption by insects and animals.
The central vacuole also functions to store proteins in developing seed cells.
In plant cells, the digestive processes take place in vacuoles.
Plasmodesmata
Plasmodesmata(singular = plasmodesma) are junctions between plant cells,
Neighboring plant cells cannot touch one another because they are separated by the cell walls
The Plasmodesmata are numerous channels that pass between the cell walls of adjacent plant cells,
They serve to connect the cytoplasm , signal molecules and transport the nutrients from one plant cell to another.
Organelles/ cell structures specific for Animal cell
The Centrosome
The centrosome is a microtubule-organizing center. It is found near the nuclei of animal cells and contains a pair of centrioles,
The two centrioles lie perpendicular to each other.
Each centriole is a cylinder of nine triplets of microtubules. Non tubulin serves to hold the microtubule triplets .
The microtubule originate from the centrosome .
The centrosome replicates itself before a cell division.
The centrioles pull the duplicated chromosomes to opposite ends of the dividing cell.
The exact function of the centrioles in cell division is however not clear as cells that have had the centrosome removed can still divide; and plant cells, which lack centrosomes, are capable of cell division.

“Centriole structure” by Libre Text biology is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
Lysosomes
The lysosomes are the cell’s “garbage disposal units ” .
The lysosomes contain enzymes that aid the breakdown of proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, and even worn-out organelles.
These enzymes are active at a much lower pH than that of the cytoplasm. Therefore, the pH within lysosomes is more acidic than the pH of the cytoplasm.
Many reactions that take place in the cytoplasm could not occur at a low pH,
this is the advantage of compartmentalizing the eukaryotic cell into organelles .
“lysosome “ by Open stax is licensed under CC BY 4.0
Extracellular Matrix of Animal Cells
Most animal cells release materials into the extracellular space.
The primary components of the extra cellular matrix are glycoproteins and the protein collagen. Collectively, these materials are called the extracellular matrix .
Their function include :
- Hold the cells together to form a tissue
- Allows the cells within the tissue to communicate with each other.
Test your understanding of the plant cell structure.
Test your understanding of the cell organelles
A polysaccharide comprised of glucose units
The process by which plants make their own food like sugar and starch using carbon dioxide ,water and sunlight and liberate oxygen
Organisms capable of making their own food
Organisms that depend on other organisms for their food
A set of interconnected and stacked fluid filled membrane sacs seen within the inner membrane of the chloroplast
Each stck of thylakoid
Fluid within the inner membrane of the chloroplast that surrounds the grana

